What started as a minor ingrown hair quickly turned into a painful, swollen lump – sound familiar?
An ingrown hair can turn into a hard lump under the skin when the hair grows back into the skin, leading to irritation or infection. These lumps can range from small, painless bumps to large and infected cysts, causing discomfort, severe pain, and anxiety. If you’re dealing with these unpleasant lumps, you’re not alone.
In this guide, I’ll explore everything you need to know about these bothersome bumps, from their causes and symptoms to the best treatment options and preventive measures. Whether you’re looking for quick home remedies or professional advice, I’ve got you covered.
What Causes an Ingrown Hair to Turn into a Lump?
Shaving, waxing, and wearing tight clothing can cause ingrown hairs. The hair re-enters the skin or fails to grow out of the follicle, leading to irritation, inflammation, or infection. Here at Feminine Health, our team believes understanding these causes helps you manage and prevent painful lumps under the skin in the future.
Physical Irritation
Shaving too closely or using a dull razor can irritate the skin, increasing the risk of ingrown hairs. Tight clothing and friction also cause ingrown hairs by pressing the hair back into the follicle. Waxing and tweezing forcibly remove hairs, leading to potential misdirection as they regrow.
Biological Factors
Curly, coarse, or thick hair increases the likelihood of ingrown hairs. Dry skin restricts hair growth and exacerbates the issue. Moisturizing your skin can help the hair grow out naturally rather than curling back inwards.
Inflammation and Infection
When a hair grows back into the skin, the immune system responds, causing redness, swelling, and a hard lump. If bacteria enter the follicle, infection can occur, resulting in a more prominent, painful lump.

Symptoms of an Ingrown Hair Lump
Identifying symptoms early can prevent further complications and promote quicker healing.
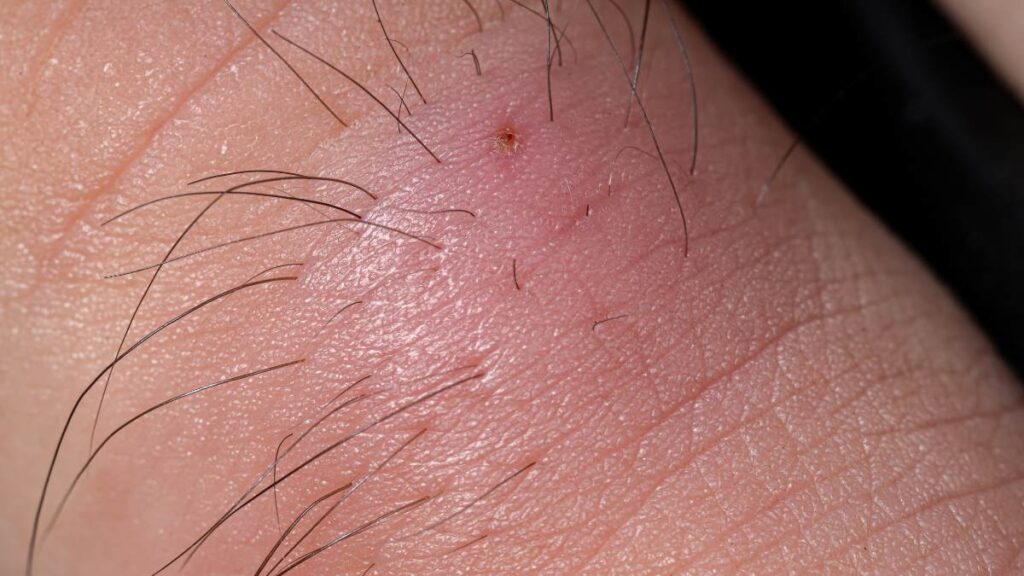
Redness and Swelling
A lump from an ingrown hair is often red and swollen. The skin around the ingrown hair becomes inflamed as the body reacts to the foreign object. The area may also feel warm to the touch.
Pain and Tenderness
Pain and tenderness accompany ingrown hair lumps. These symptoms intensify if the lump becomes infected. The pain may be constant or felt when touching or moving the affected area.
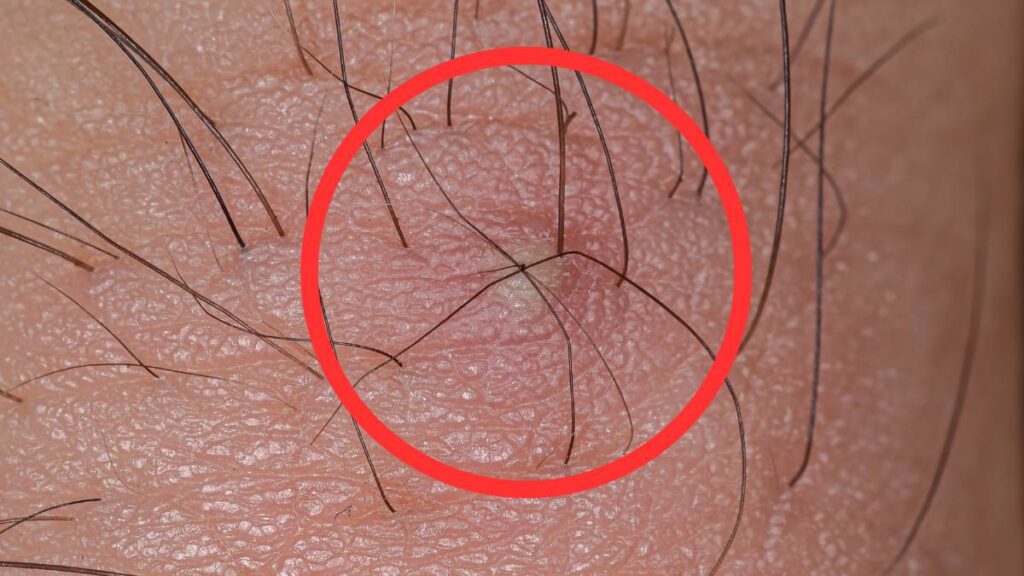
Hard Lump
The classic sign of an ingrown hair turning into a hard lump is a firm, raised bump under the skin. The lump might vary in size, from small and barely noticeable to large and prominent.
Possible Discharge
If the lump is infected, pus or other discharge might be present. This symptom suggests the body is fighting an infection within the follicle.
Identifying an Ingrown Hair Cyst
Distinguishing between a standard ingrown hair and an ingrown hair cyst can guide proper treatment.
- Size and Texture: Ingrown hair cysts are typically larger and harder than regular ingrown hairs. They may feel more solid and immovable under the skin.
- Fast Growth: Unlike typical ingrown hairs, cysts develop quickly, growing in size over a short period. Pay attention if the lump enlarges and becomes more painful.
- Presence of a Hair: In some cases, you might see the hair trapped under the skin in the cyst. This can help confirm that the lump is indeed an ingrown hair cyst.
- Infection Indicators: Signs of infection, such as redness, warmth, and pus, often accompany cysts. If these symptoms appear, the lump likely progresses beyond a simple ingrown hair.
Complications of Untreated Ingrown Hairs
Without proper treatment, ingrown hairs can lead to several complications.
Infection
Untreated ingrown hairs can become infected, causing more significant pain, redness, and swelling. Severe infections may require more intensive treatment.
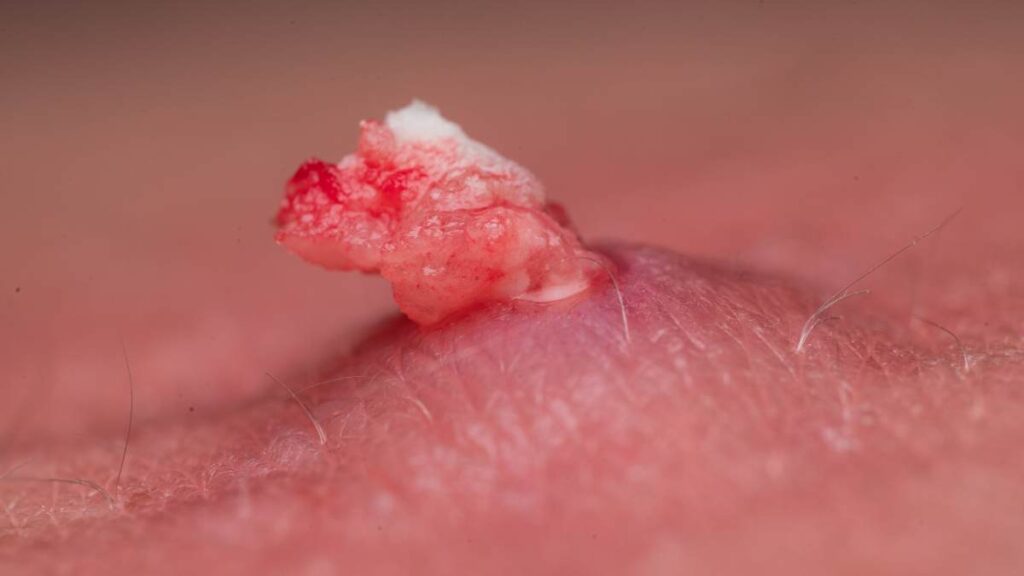
Abscess Formation
An abscess, a painful collection of pus, may form when an ingrown hair gets severely infected. Abscesses often need draining and further medical intervention.
Permanent Scarring
Untreated ingrown hairs can lead to permanent scarring and skin discoloration. This can lead to lasting changes in skin texture and appearance.
Treatment Options for Ingrown Hair Lumps
Managing ingrown hair lumps involves several approaches, ranging from home remedies to medical interventions.
Home Treatments
Warm Compress
Applying a warm compress can soothe irritation and reduce swelling. This helps the hair work its way out of the skin naturally.
Exfoliation
Gently exfoliating the affected area removes dead skin cells, preventing hair from becoming trapped. Use a mild scrub or loofah.
We recommend the Kushae Waxing & Shaving Kit which contains everything you need prevent ingrown hairs after waxing and shaving.
Tea Tree Oil
Tea tree oil has antimicrobial properties that reduce inflammation and fight infection. Apply diluted tea tree oil to the lump to calm irritation.
Over-the-Counter Solutions
- Topical Antibiotics: Applying an over-the-counter antibiotic cream can prevent or treat minor infections. Look for products with active ingredients like bacitracin.
- Retinoids: Topical retinoids promote cell turnover and prevent hairs from becoming trapped by dead skin cells. These might require a prescription from a dermatologist.
Medical Interventions
Minor Surgical Procedures
In severe cases, a healthcare professional may need to excise the lump. This involves a minor surgical procedure to remove the ingrown hair and the surrounding cyst:
Antibiotics
For infected ingrown hair lumps, a course of antibiotics may be necessary to clear the infection. This treatment should reduce symptoms and prevent the spread of bacteria.
Should you see a Doctor?
If you notice your lump isn’t improving within a week or two, and home treatments aren’t effective, you should consult a healthcare provider. Persistent symptoms, such as ongoing pain, swelling, or redness, signify deeper issues that might require medical treatment.
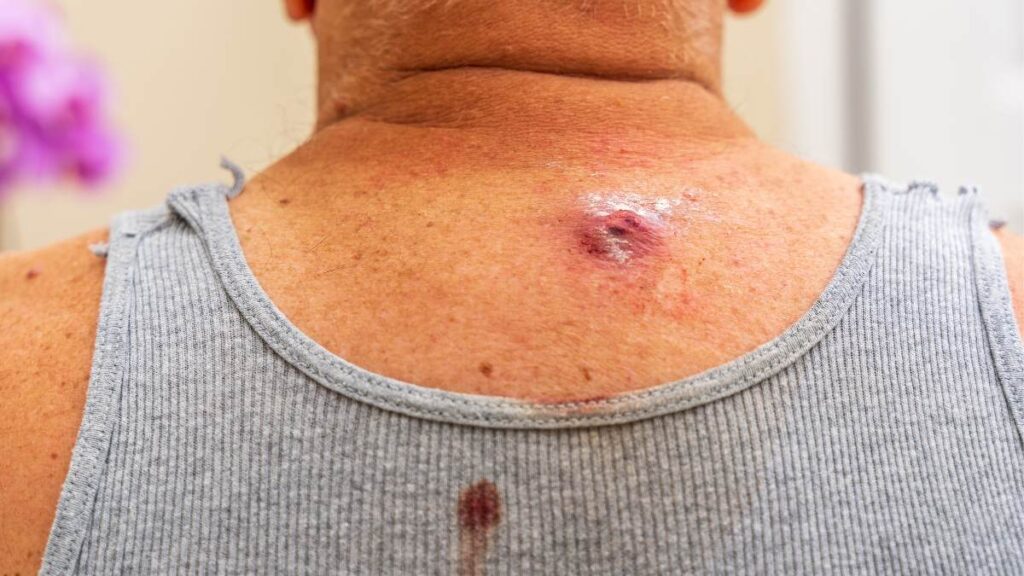
Signs of Infection
Watch for signs of infection, including:
- Increased redness: The area around the lump becomes more inflamed.
- Pus or discharge: Presence of yellow or green pus.
- Fever: Elevated body temperature indicating infection spread.
Severe Discomfort
If the discomfort from the lump becomes unbearable or restricts daily activities, seeking professional assistance will provide relief.
The healthcare provider may offer treatments that address the underlying cause effectively.
Large or Growing Lump
A lump that continues to grow or is significantly larger than a typical ingrown hair should be evaluated. These signs suggest complications beyond home remedies.
Preventing Ingrown Hairs and Lumps
Preventing ingrown hairs starts with good skin care practices and proper grooming techniques.
Proper Shaving Techniques
Shaving the right way reduces the risk of ingrown hairs:
- Use a sharp razor: It minimizes hair tugging and prevents irritation.
- Shave in the direction of hair growth: This prevents the hair from being forced back into the skin.
- Moisturize the skin: Use shaving creams or gels to keep the skin hydrated and soft.
Exfoliation
Regular exfoliation removes dead skin cells, preventing blockage:
- Gently exfoliate: Use mild scrubs or exfoliation gloves.
- Regular routine: Incorporate exfoliation into your weekly routine for optimal results.
Wear Loose Clothing
Tight clothing can rub against the skin, causing friction and encouraging hair to grow back into the skin:
- Opt for loose-fitting clothes: Especially after shaving or waxing.
Professional Hair Removal
Consider professional hair removal techniques:
- Laser hair removal: Reduces hair growth over time and minimizes ingrown hairs.
- Electrolysis: Targets hair roots, offering a more permanent solution.
Home Remedies for Soothing Ingrown Hair Lumps
Home remedies include warm compresses, antiseptic solutions like tea tree oil to alleviate discomfort and promote healing:
Warm Compress
A warm compress helps:
- Reduce inflammation: Apply several times a day.
- Draw out the hair: Makes it easier for the hair to emerge through the skin.
Tea Tree Oil
Tea tree oil is known for its antimicrobial and anti-inflammatory properties:
- Dilute and apply: Mix with a carrier oil to prevent skin irritation.
- Reduce infection risk: Promotes healing and prevents bacteria buildup.
Aloe Vera
Aloe vera soothes irritated skin:
- Apply gel directly: Reduces redness and inflammation.
- Natural healing properties: Helps in the recovery process.
Essential Oil Blends
Blending essential oils can enhance their benefits:
- Lavender or chamomile: Known for soothing and calming properties.
- Apply carefully: Dilute with a carrier oil to prevent irritation.
Differentiating Between Ingrown Hairs and Other Skin Conditions
Understanding the differences between ingrown hairs and other skin conditions helps in proper identification and treatment.
Ingrown Hairs vs. Boils
Ingrown Hairs:
Boils:
- No visible hair: Pus-filled lump.
- Severe pain: Can be larger and require draining.
Ingrown Hairs vs. Pimples
Ingrown Hairs:
- Hair involvement: Hair trapped causes the bump.
- Localized swelling: Redness around the affected follicle.
Pimples:
- No hair involvement: Usually caused by clogged pores.
- May occur anywhere: Including areas without hair follicles.
Ingrown Hair Cysts
Ingrown hair cysts are often larger and harder:
- Firm texture: Unlike softer pimples.
- Possible discharge: If infected, resulting in pus.
Regularly checking your skin helps in early identification and treatment of any conditions.
Conclusion
Preventing and treating ingrown hair lumps is vital for maintaining healthy skin. Recognizing symptoms, applying effective home treatments, and adopting preventative habits can make a significant difference. If symptoms persist or worsen, professional intervention ensures proper care. Stay proactive in your skincare routine to avoid future occurrences.
For more insightful health information and tips, visit Feminine Health.